Industries such as automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and metal fabrication heavily use robots to improve efficiency and maintain consistent quality.
Industrial robots, first introduced in the mid-20th century, have drastically evolved to become the cornerstone of modern manufacturing. Their precision, speed, and efficiency allow businesses to meet the rising demands of global markets. As industries aim for cost-effective solutions, robotics presents an ideal path toward sustainable growth and innovation.
Industrial Manufacturing Robots Shaping the Future of Production

Industrial manufacturing robots are revolutionizing production lines by enhancing precision, efficiency, and scalability. These advanced machines streamline operations, reduce human error, and optimize costs, ensuring businesses remain competitive globally.
Robots in Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide

In the manufacturing sector, it handle repetitive, dangerous, and complex tasks. They perform assembly, welding, material handling, and quality inspection functions. Companies achieve higher productivity and maintain consistent quality standards by automating these processes.
Leading Industrial Robot Manufacturers Driving Innovation
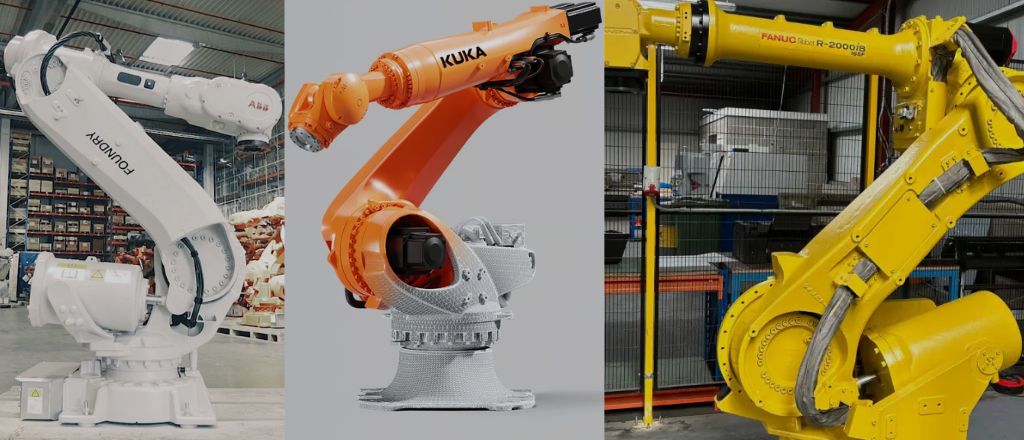

Companies like ABB, KUKA, and FANUC are at the forefront of robotic innovation. These manufacturers provide cutting-edge solutions tailored to diverse industrial needs, from automotive assembly to electronics production.
Key Industrial Robotic Arm Manufacturers Shaping the Industry
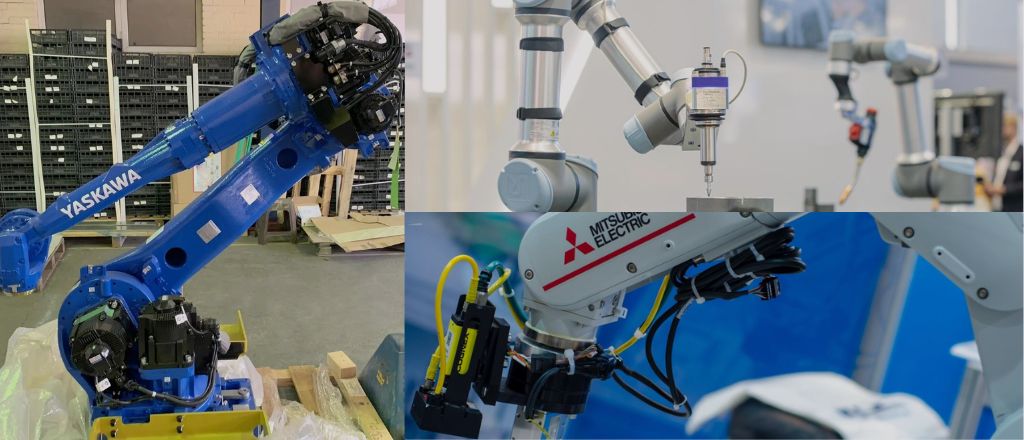

Robotic arms, designed for flexibility and precision, are vital in modern manufacturing. Leaders such as Yaskawa, Mitsubishi Electric, and Universal Robots produce advanced robotic arms catering to various industries, enhancing productivity and adaptability.
Mitsubishi Electric's MELFA robots are known for their compact design and high-speed performance, ideal for electronics and small-part assembly. Universal Robots' collaborative robots (cobots) prioritize safety and flexibility, enabling humans and robots to work side-by-side in dynamic environments. These advancements showcase the growing potential of robotic arms to reshape traditional workflows.
Chinese Industrial Robot Manufacturers: Global Leaders in Automation
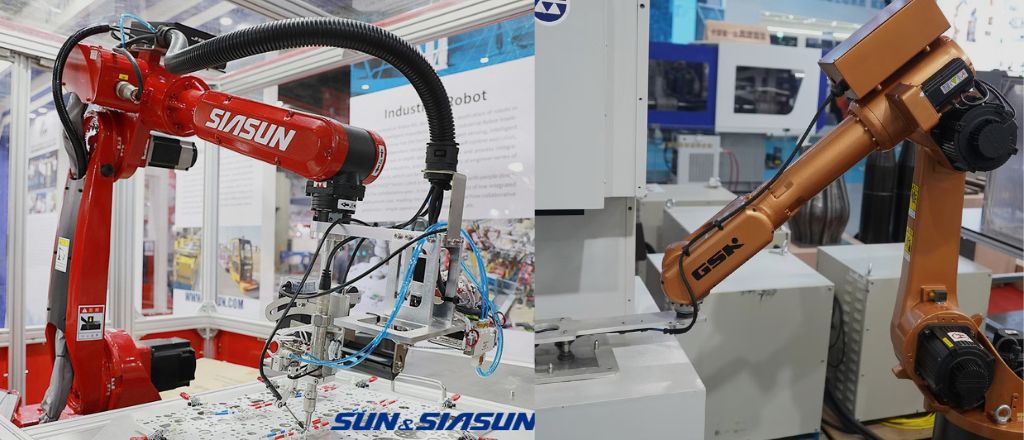

China is a dominant player in robotics, with companies like Siasun and GSK Robotics setting global benchmarks. These manufacturers offer cost-effective solutions catering to domestic and international markets, making automation accessible to businesses worldwide.
Industries that Use Robots in Manufacturing for Increased Efficiency
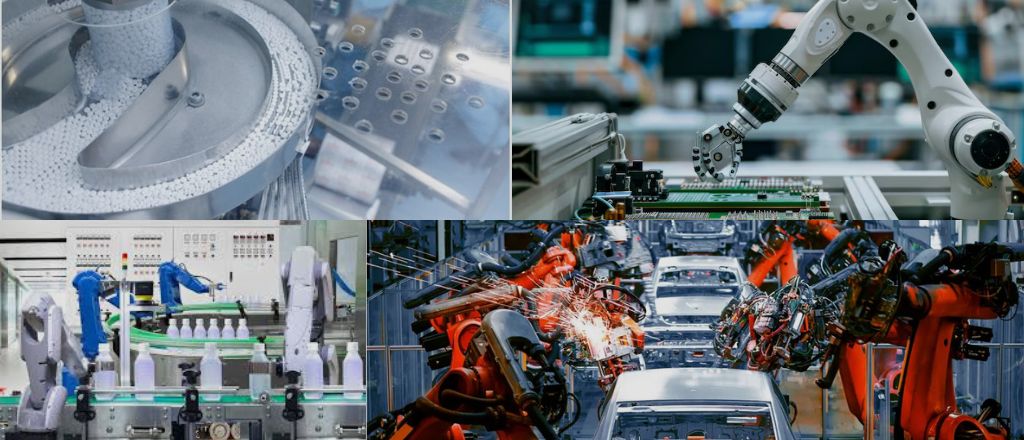
They are integral to the automotive, electronics, pharmaceuticals, and food processing industries. By leveraging robotics, these sectors improve production speed, ensure quality consistency, and meet growing consumer demands.
The automotive industry uses robotics for assembly line tasks such as welding and painting. In electronics, delicate components are assembled with unparalleled precision. Pharmaceutical companies leverage robotics for drug manufacturing and packaging, ensuring safety and consistency. The food industry benefits from automation in sorting, packaging, and quality control, reducing waste and increasing throughput. Metal fabrication processes like cutting, bending, and welding are executed with superior accuracy, driving efficiency in construction and infrastructure development.
Japanese Industrial Robot Manufacturers: Pioneers of Advanced Robotics
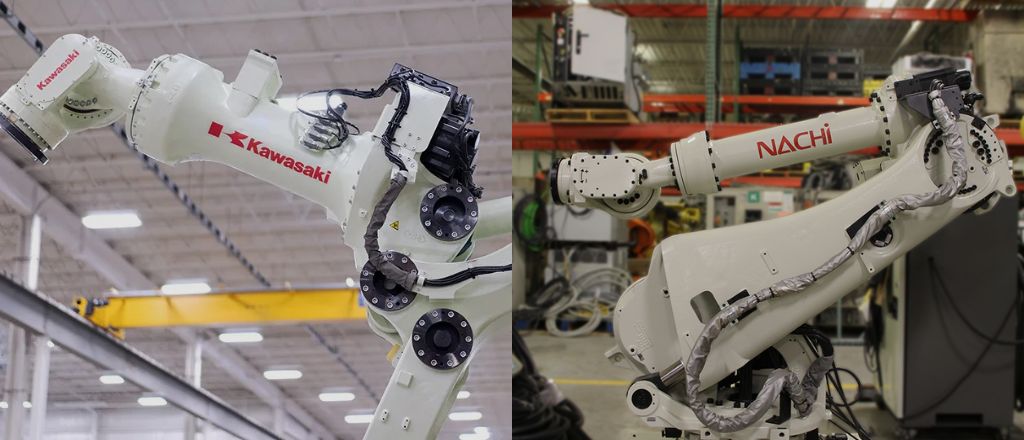
Japan's robotics industry, led by giants like Kawasaki and Nachi, emphasizes precision and innovation. These manufacturers are known for their high-quality system that enable seamless integration into complex manufacturing processes.
Robotic Process Automation in the Manufacturing Industry: Revolutionizing Workflows

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) simplifies workflows by automating routine administrative tasks. From inventory management to scheduling, RPA ensures operational efficiency and reduces manual intervention.
Top 10 Industrial Robot Manufacturers Dominating the Market
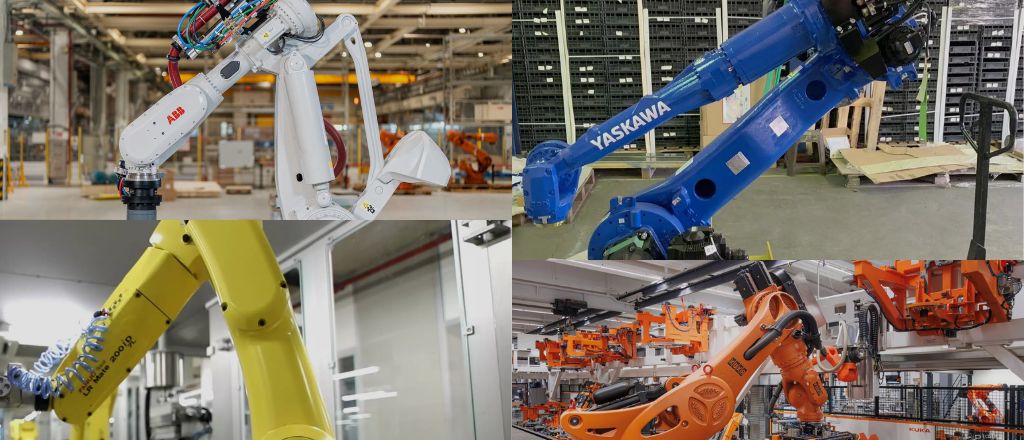

Key players such as ABB, FANUC, KUKA, and Yaskawa dominate the global robotics market. These companies continuously invest in research and development to provide innovative solutions that meet evolving demands.
US Industrial Robot Manufacturers: Innovators in Automation Solutions
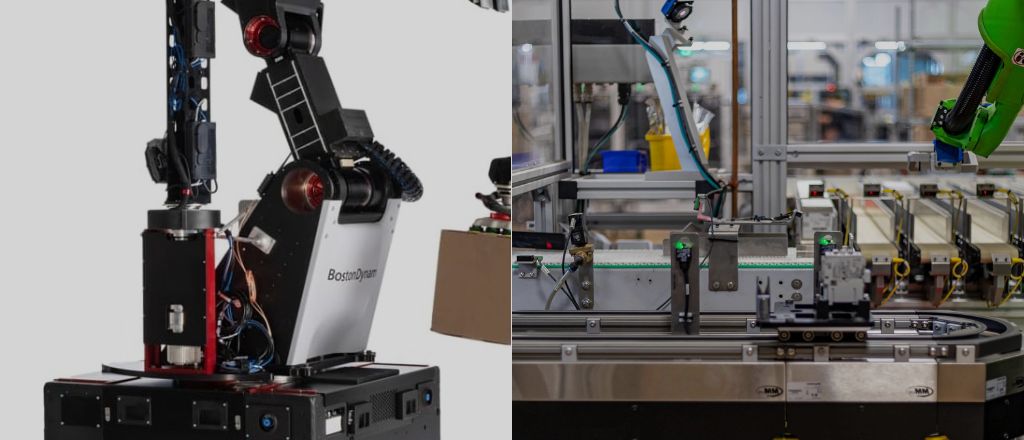

American manufacturers like Boston Dynamics and Rockwell Automation are known for their groundbreaking technologies. Their contributions include advanced robotics systems that cater to complex challenges, driving the automation revolution forward.
Let's Ask the Expert Trevor
The six major types are articulated, SCARA, delta, Cartesian, cylindrical, and collaborative (cobots) robots.
An example is the FANUC M-20iA, commonly used in assembly and material handling tasks in manufacturing.
FANUC is considered one of the largest industrial robot manufacturers globally, leading in sales and innovation.
Automated machines are utilized in various ways to enhance efficiency and improve quality in industry and society. In manufacturing, they assemble products with precision and consistency. In logistics, automated machines are used for sorting, packaging, and warehouse automation. In healthcare, they assist in surgeries, deliver medications, and provide support for elderly care. In agriculture, automated machines help with planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops. Additionally, in public safety, they perform tasks like bomb disposal, search and rescue operations, and surveillance. These applications reduce human risk, increase productivity, and ensure higher standards of safety and service across diverse fields.
Robots are widely used in manufacturing industries to improve efficiency, precision, and safety. They perform repetitive tasks such as assembly, welding, painting, and packaging, reducing human error and production time. Robots are also employed in material handling, quality inspection, and palletizing, ensuring consistency and accuracy. Advanced robotics, including collaborative robots (cobots), work alongside humans to enhance productivity in complex operations. By automating hazardous tasks, robots protect workers from injury and enable them to focus on higher-value work. Integration with AI and IoT further optimizes manufacturing processes, allowing real-time monitoring and adaptability to changing production needs.
The most commonly used robot in manufacturing is the articulated robot, thanks to its versatility and precision. These robots have rotary joints, providing them with a wide range of motion similar to a human arm. Articulated robots excel in tasks such as welding, assembly, and material handling. They are popular due to their adaptability in handling complex operations in diverse industries, including automotive, electronics, and aerospace. Their ability to perform tasks at high speed and accuracy makes them a valuable asset in automation. Collaborative robots (cobots) are also increasingly common, enabling safe, efficient teamwork with human workers.
Industries utilize various types of robots based on specific tasks. Common types include articulated, SCARA, Cartesian, cylindrical, and collaborative (cobots). Articulated robots, resembling a human arm, are widely used for welding, assembly, and material handling. SCARA robots excel in pick-and-place operations and precision assembly tasks. Cartesian robots, operating on three linear axes, are ideal for tasks requiring accuracy, like 3D printing and packaging. Cylindrical robots are used for machine tending and die-casting. Collaborative robots (cobots) are increasingly popular, working safely alongside humans to enhance productivity in industries like automotive, electronics, and manufacturing.
A modern industrial robot is an advanced, automated machine designed to perform tasks with precision, efficiency, and speed. It typically integrates sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) for enhanced adaptability. Unlike traditional robots, modern robots can perform complex operations, such as quality inspection, intricate assembly, and 3D printing. They are often equipped with collaborative features to safely work alongside humans, minimizing the need for physical barriers. These robots are widely used in industries like manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and agriculture, revolutionizing workflows with capabilities like predictive maintenance, real-time decision-making, and adaptability to varied environments.

